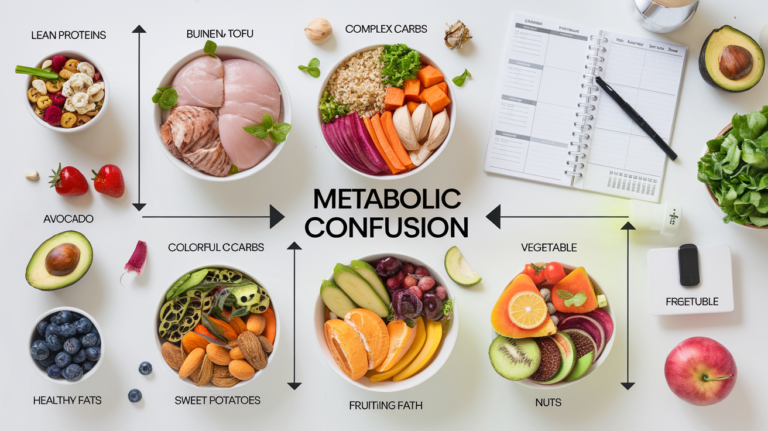
Metabolic Confusion Diet has recently gained attention as a game-changing approach to weight management and overall health. The idea is simple: strategically alternate between periods of high-calorie and low-calorie days to keep the metabolism working optimally. But does this approach really work? What is the science behind it? Let’s dive into the concept of metabolic confusion and explore how this diet could be a game-changer for those seeking to achieve long-lasting weight loss and improved energy levels.
1. What Is the Metabolic Confusion Diet?
At its core, the Metabolic revolves around a concept known as “calorie cycling” — alternating between high-calorie and low-calorie days. The primary goal is to disrupt the body’s ability to adapt to a single caloric intake level. When following a traditional, consistent low-calorie diet, the body can go into “starvation mode” where metabolism slows down to conserve energy. By changing calorie intake frequently, metabolic confusion aims to keep the metabolism guessing, thus preventing this slowdown. Over time, this strategy can potentially lead to more effective and sustainable weight loss while also increasing energy levels.
2. The Role of Metabolic Flexibility in Weight Loss
Metabolic flexibility is the ability of the body to efficiently switch between burning carbohydrates and fats for energy. This is a critical aspect of metabolic health. The Metabolic leverages this natural adaptability by encouraging the body to burn different sources of fuel depending on the day’s calorie intake. On high-calorie days, the body uses carbohydrates and proteins to fuel performance, while on low-calorie days, it taps into fat stores for energy. By keeping the body flexible, metabolic confusion can enhance fat oxidation, prevent muscle loss, and improve metabolic efficiency.
3. How the Metabolic Differs from Traditional Dieting
Traditional dieting usually revolves around a steady reduction in calories over a period of time, often leading to slower metabolism, weight loss plateaus, and feelings of deprivation. The Metabolic , on the other hand, introduces a dynamic shift in calorie intake. Instead of consistently lowering calorie intake, it alternates between high- and low-calorie days. This unpredictability prevents the body from adjusting to a single level of caloric intake, thereby reducing the risk of metabolic slowdown. Additionally, this approach provides more flexibility, allowing individuals to enjoy a variety of foods while still achieving weight loss.
4. The Benefits of Metabolic Confusion
Supporters of the Metabolic argue that it offers several benefits over traditional dieting methods. These include: enhanced fat burning, preservation of lean muscle mass, and improved adherence to the diet. The alternating nature of the diet allows individuals to indulge without feeling deprived on high-calorie days, making it a more sustainable approach in the long run. Furthermore, by avoiding the metabolic slowdown that often accompanies constant calorie restriction, individuals may experience better results, including long-term weight loss, better energy levels, and improved overall health.
5. How to Implement the Metabolic
Implementing the Metabolic requires careful planning and attention to calorie intake. Generally, the diet alternates between high-calorie days and low-calorie days. On high-calorie days, individuals typically consume more nutrient-dense foods like lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats to fuel the body and restore energy. Low-calorie days are designed to create a caloric deficit, encouraging fat loss. During these days, focus on high-protein, fiber-rich foods that keep you feeling full without adding excessive calories. Additionally, balancing macronutrients is crucial for ensuring proper nutrition and energy levels on both types of days.
6. Understanding High-Calorie Days
High-calorie days are an essential part of the Metabolic . These days are designed to replenish glycogen stores, support muscle recovery, and fuel intense workouts. During these days, it is important to prioritize whole, nutrient-dense foods. Incorporating lean proteins like chicken or fish, complex carbohydrates like quinoa or sweet potatoes, and healthy fats such as avocados or olive oil can help maximize performance and recovery. High-calorie days also provide a mental break from the restrictions of low-calorie days, making the diet more enjoyable and sustainable.
7. Low-Calorie Days: The Key to Fat Burning
Low-calorie days are the foundation of fat loss in the Metabolic . By creating a calorie deficit, these days prompt the body to burn stored fat for energy. However, the focus is not solely on reducing calories but on maintaining nutritional value. On low-calorie days, the diet emphasizes high-protein, high-fiber foods such as vegetables, lean meats, and legumes to keep hunger at bay. These foods also ensure that the body is receiving the nutrients it needs while still encouraging fat loss. It is important to avoid extreme calorie reduction to prevent muscle loss and nutrient deficiencies.
8. Exercise and the Metabolic
Exercise plays a crucial role in maximizing the benefits of the Metabolic . Combining strength training with cardiovascular exercise can increase calorie burn, improve metabolic rate, and promote fat loss. On high-calorie days, individuals can use the additional energy to fuel their workouts, enhancing performance and muscle recovery. On low-calorie days, exercise can help preserve lean muscle mass while still facilitating fat burning. Additionally, regular physical activity can help maintain a balanced metabolic rate and avoid the common pitfalls of dieting, such as a plateau in progress.
9. Potential Misconceptions About the Metabolic
Despite its growing popularity, there are several misconceptions surrounding the Metabolic . Some may believe that the diet promotes unhealthy eating habits, but this is not the case. In fact, the diet encourages a balanced approach to nutrition, prioritizing whole foods and nutrient-dense options. Others may think that metabolic confusion guarantees rapid weight loss, but results can vary depending on individual factors such as activity level, metabolism, and adherence to the plan. It’s also important to remember that any diet, including metabolic confusion, should be part of a broader, sustainable approach to health and wellness.
10. Who Should and Should Not Try the Metabolic ?
While the Metabolic can be effective for many, it may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with specific health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or thyroid disorders should consult a healthcare provider before starting this diet. Pregnant or breastfeeding women may also need to avoid restrictive eating patterns. Furthermore, those with a history of eating disorders should exercise caution. It is always recommended to seek medical advice before making significant dietary changes, especially for those with pre-existing health conditions.
11. How to Stay Consistent on the Metabolic
Staying consistent on the Metabolic requires a combination of planning, flexibility, and mindfulness. Setting realistic goals and creating a meal plan that aligns with both high-calorie and low-calorie days can help ensure adherence. Additionally, keeping a food diary or using an app to track calories can help you stay on track and monitor your progress. Flexibility is key, as life events may require adjustments to your schedule. Listening to your body and making mindful choices about food will also improve your chances of success.
12. Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Like any diet, the Metabolic has its challenges. One common pitfall is overeating on high-calorie days, which can undermine the benefits of the diet. Another challenge is under-consuming on low-calorie days, which may lead to energy depletion or muscle loss. To avoid these issues, plan meals carefully and monitor portion sizes. Additionally, it’s essential to maintain a balanced intake of macronutrients on both high- and low-calorie days to ensure you’re receiving adequate nutrition.
13. The Importance of Macronutrient Balance
Post Disclaimer
The information contained in this post is for general information purposes only. The information is provided by Daily recipes and while we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the post for any purpose.